The frontend for chatbots shapes user experience, engagement, and trust. By combining intuitive UI, adaptive design, and real-time feedback, businesses can create conversational interfaces that feel natural, responsive, and drive meaningful interactions.
Why Frontend Matters More Than Ever in Chatbots
The rise of conversational AI has transformed how users interact with brands, platforms, and digital services. While backend intelligence often gets the spotlight, the frontend for chatbots plays an equally critical role in determining whether conversations succeed or fail. A chatbot may be powered by sophisticated algorithms, but if users struggle to interact with it, engagement drops fast.
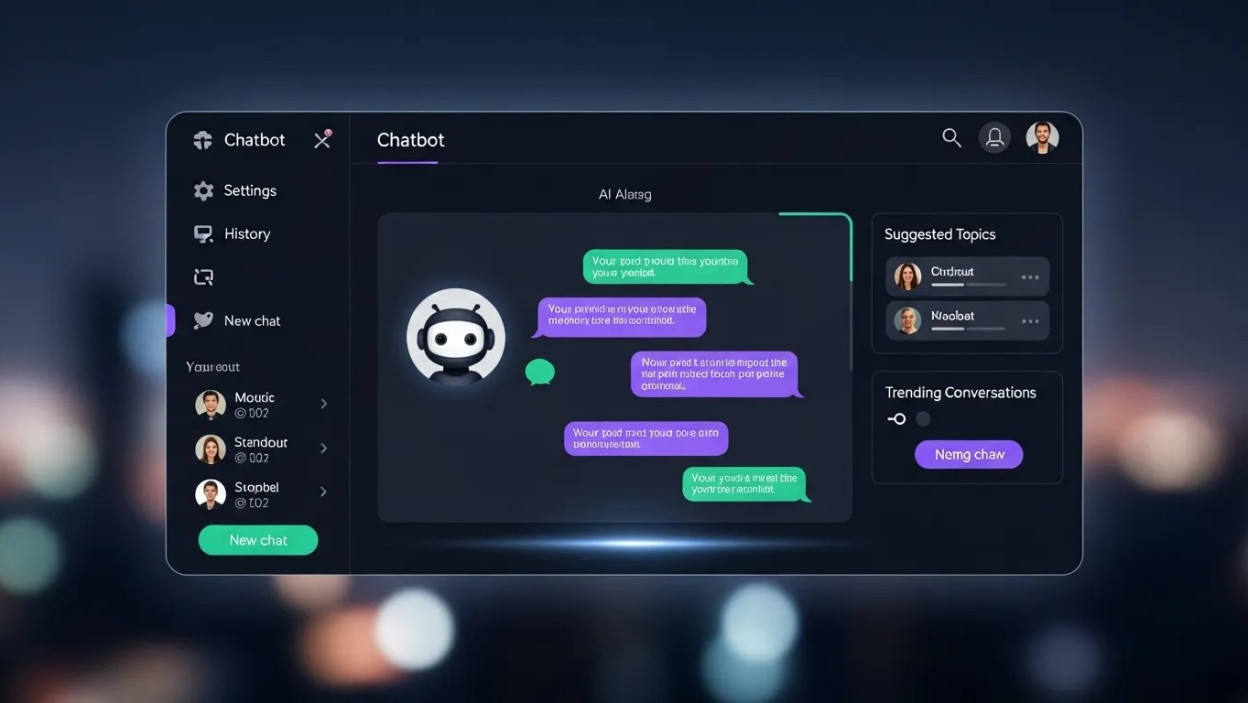
The frontend for chatbots serves as the bridge between human intent and machine intelligence. It shapes first impressions, guides conversation flow, reduces friction, and builds trust. From message bubbles and buttons to tone, spacing, and response timing, every UI decision directly impacts how users perceive and continue a conversation.
As users become more accustomed to conversational interfaces, expectations rise. They want chat experiences that feel intuitive, responsive, and human-like. This makes frontend design not just a visual concern but a behavioral and psychological one.
Understanding User Psychology in Conversational Interfaces
Before diving into layouts or components, it’s essential to understand how users think and behave in chat environments. Conversations are not linear forms; they are dynamic, emotional, and context-driven.
Users subconsciously expect chat interfaces to mimic human conversation patterns. Delays feel awkward, robotic language feels cold, and cluttered interfaces feel overwhelming. The frontend for chatbots must reduce cognitive load while encouraging users to continue interacting.
Key psychological triggers include:
-
Familiar messaging patterns (similar to WhatsApp or Messenger)
-
Clear visual hierarchy to guide attention
-
Predictable interaction behavior
-
Emotional safety through friendly language and design
When frontend decisions align with these triggers, conversations feel effortless rather than forced.
Core Components of an Effective Chatbot Frontend

Message Layout and Visual Hierarchy
Message bubbles are the foundation of any chatbot interface. Their shape, spacing, and alignment influence readability and emotional tone. Proper contrast and padding make conversations easy to scan, especially on mobile devices.
A well-structured frontend for chatbots ensures users instantly know who is speaking, what requires action, and where the conversation is heading.
Input Fields and Interaction Controls
Text input areas should feel accessible and responsive. Placeholder text, micro-animations, and subtle cues can guide users on what to type next. Buttons, quick replies, and carousels help reduce user effort by offering structured responses.
These elements act as conversation accelerators, preventing confusion and hesitation.
Chatbot UI Design Principles That Drive Engagement
A strong interface is built on consistency and clarity. Chatbot UI Design focuses on aligning visual elements with conversational intent. Fonts should be readable, colors should reinforce brand identity without distraction, and icons should communicate meaning instantly.
Consistency across conversations builds familiarity, while minimalism prevents overload. When users don’t have to think about how to interact, they focus entirely on the conversation itself.
Structuring Conversations Through Frontend Logic
Frontend design doesn’t just display messages; it subtly structures conversations. Visual grouping, progressive disclosure, and response timing all influence how users move through dialogue.
For example:
-
Breaking long responses into smaller chunks improves retention
-
Typing indicators create anticipation and realism
-
Contextual UI elements prevent users from feeling lost
The frontend for chatbots acts as a silent guide, shaping the conversation without explicit instructions.
Designing for Different Chatbot Use Cases
Not all chatbots serve the same purpose. Informational bots, support bots, and transactional bots each require different frontend strategies.
Informational Chatbots
These rely heavily on readability and content hierarchy. Clear formatting, expandable sections, and quick navigation options are essential.
Support Chatbots
Trust and clarity are critical. Status indicators, confirmation messages, and escalation options should be clearly visible.
Transactional Chatbots
Speed and precision matter most. Buttons, forms, and validation feedback must be immediate and intuitive.
Each scenario demands thoughtful frontend customization to match user intent.
How to Design Chatbot UX for Seamless Flow
How to Design Chatbot UX starts with mapping user journeys before designing interfaces. Understanding entry points, common questions, and exit paths helps create smooth conversational flows.
Good UX ensures:
-
Users always know what to do next
-
Errors are handled gracefully
-
Conversations feel purposeful, not endless
The frontend for chatbots must support these flows visually, reinforcing progress and reducing uncertainty.
Responsive Design and Cross-Platform Consistency
Users interact with chatbots across devices: mobile, desktop, and embedded apps. A responsive frontend adapts layouts, spacing, and controls without breaking the conversation experience.
Touch-friendly buttons, adaptive text sizes, and platform-specific behaviors ensure usability everywhere. Consistency across platforms builds confidence and reduces learning curves.
Integrating Intelligence Without Overwhelming Users
Advanced AI capabilities should feel invisible to users. Even when powered by Deep Learning Chatbots, the frontend must keep interactions simple and understandable.
Avoid exposing system complexity. Instead, present insights, suggestions, and responses in a natural conversational manner. The goal is to make intelligence feel human, not technical.
Voice Interfaces and the Evolution of Frontend Design

As Voice Activated Chatbots become more common, frontend design expands beyond screens. Visual cues now support voice interactions, showing listening states, confirmations, and contextual information.
Hybrid interfaces that combine voice and visual feedback enhance accessibility and user comfort. Frontend design must evolve to support these multimodal experiences seamlessly.
Emotional Design and Trust Building
Trust is built through consistency, transparency, and empathy. Friendly microcopy, polite error handling, and reassuring feedback make users feel understood.
Subtle design choices, such as soft colors or conversational spacing, can reduce anxiety and encourage longer interactions. Emotional design turns functional conversations into meaningful experiences.
Performance Optimization and Perceived Speed
Even slight delays can disrupt conversational flow. Frontend optimization focuses on perceived speed as much as actual performance.
Techniques include:
-
Skeleton loaders
-
Typing animations
-
Progressive message rendering
These elements keep users engaged while systems process responses, maintaining conversational rhythm.
Frontend Accessibility in Chatbot Experiences
Accessibility ensures conversations are inclusive. Screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, and sufficient contrast are essential components of a responsible frontend for chatbots.
Designing for accessibility not only broadens reach but also improves overall usability for all users.
Data Feedback and Conversation Improvement
Frontend interfaces can collect valuable behavioral data without being intrusive. Click patterns, drop-off points, and interaction timing reveal where conversations succeed or fail.
These insights help refine UI elements and conversational flows over time.
Chatbots in Marketing and Engagement Contexts
When chatbots are used for engagement and growth, frontend design must balance usefulness with subtle persuasion. AI Driven Chatbot Marketing relies on interfaces that feel helpful rather than pushy.
Clear opt-ins, respectful timing, and value-driven interactions ensure users stay receptive.
Social Platforms and Conversational Interfaces

How Social Media Chatbots operate depends heavily on platform-specific frontend constraints. Each platform has unique UI rules, interaction patterns, and user expectations.
Designing within these ecosystems requires adapting frontend elements while maintaining brand consistency and conversational clarity.
Comparing Key Frontend Elements Across Use Cases
| Use Case | Primary UI Focus | Key Interaction Element |
|---|---|---|
| Informational | Readability | Expandable messages |
| Support | Trust & clarity | Status indicators |
| Marketing | Engagement | Quick replies |
| Voice-based | Feedback cues | Listening indicators |
This comparison highlights how frontend priorities shift based on chatbot goals.
Future Trends in Chatbot Frontend Design
As conversational AI matures, frontend design will continue to evolve. Personalization, adaptive interfaces, and emotion-aware UI elements will become more common.
The frontend for chatbots will increasingly act as a living interface, adjusting tone, layout, and interaction style based on user behavior and context.
Personalized Chatbot Interfaces
In today’s digital world, users expect conversations tailored to their preferences. A personalized frontend for chatbots enhances engagement by adapting to user behavior, past interactions, and preferences. Custom greetings, context-aware responses, and dynamic UI elements make users feel recognized and understood. By analyzing prior interactions, the chatbot can proactively suggest options, reducing friction in decision-making. Moreover, personalization extends to visuals, such as theme selection and layout adjustments, which increase comfort and readability. A well-structured frontend for chatbots ensures that these personalized experiences are smooth, consistent, and intuitive, creating an environment where users are more likely to complete tasks and maintain long-term engagement with the platform.
Gamification Elements in Chatbot Design
Gamification can significantly boost interaction rates when integrated into the frontend for chatbots. Features like progress bars, achievement badges, and interactive quizzes make conversations more engaging and enjoyable. Users perceive the interface as fun and rewarding, which encourages repeated use. In addition, gamification elements subtly guide user behavior toward desired outcomes without appearing manipulative. Thoughtful placement of these UI components ensures they complement the conversational flow rather than interrupt it. When combined with clean message layouts and accessible input options, gamified frontend designs create a more immersive experience that keeps users motivated, actively participating, and more likely to trust the chatbot as an informative and interactive tool.
Multi Language and Localization Support
Global audiences require chatbots that can communicate in multiple languages. Frontend for chatbots must accommodate localization by dynamically adjusting interface elements, text directions, and date/time formats. Language selection menus should be easily accessible, and translated messages need to maintain the same visual hierarchy to preserve readability. Supporting diverse languages also includes adapting icons, colors, and cultural symbols to ensure comfort and clarity for all users. Properly designed multilingual frontends not only expand reach but also enhance user experience by making interactions natural and inclusive. Businesses leveraging localized conversational interfaces can build stronger relationships and increase engagement in international markets.
Real-Time Feedback and Interactive Prompts

Real-time feedback is essential for maintaining conversation momentum. Frontend for chatbots can include visual indicators such as typing animations, message status checks, and hover prompts to reassure users that their input is being processed. Interactive prompts, like suggested replies or menu options, reduce effort and guide users through complex conversations. Timely feedback reduces confusion and builds trust, which increases completion rates for tasks or surveys. Furthermore, these dynamic interface elements can adapt based on user responses, offering contextually relevant suggestions. By prioritizing real-time feedback in the frontend, chatbots provide smoother, more human-like interactions that feel responsive and engaging.
Adaptive Interface Based on User Behavior
An advanced frontend for chatbots can adapt to individual user behavior patterns. By monitoring interaction frequency, preferred response styles, and navigation habits, the interface can dynamically adjust to better meet user expectations. For instance, frequently used quick replies can be highlighted, while less relevant options are minimized. Behavioral adaptation extends to layout, message pacing, and input guidance, enhancing overall usability. This not only creates a sense of familiarity but also reduces cognitive load, making conversations more efficient. Adaptive frontends increase user satisfaction and retention by offering interfaces that evolve alongside the user, providing personalized guidance without requiring explicit configuration.
Security and Privacy Considerations in Frontend Design
Users are increasingly aware of digital privacy and security concerns. Frontend for chatbots must transparently communicate data handling practices through clear prompts, consent forms, and easily accessible settings. Secure input fields, masked data entry, and notification of sensitive operations reassure users. Visual cues and consistent interface design further reinforce trust. By integrating security-focused elements seamlessly, the frontend enhances the perception of reliability without disrupting conversational flow. Additionally, privacy-conscious designs support compliance with global regulations, such as GDPR. A thoughtful frontend ensures users feel safe sharing information, which is essential for maintaining engagement and long-term usage.
Multi Modal Frontends: Beyond Text
Modern chatbots increasingly combine text, voice, and visual elements. A multi-modal frontend for chatbots allows users to switch effortlessly between input methods. For example, text input can be supplemented with voice commands or interactive cards, enhancing accessibility and user convenience. Visual cues support voice interactions by indicating when the system is listening, processing, or providing feedback. Multi-modal designs also accommodate diverse user preferences, making conversations more inclusive. The frontend ensures seamless transitions between modes, maintaining consistency in layout and behavior. By supporting multiple interaction channels, chatbots become more versatile, responsive, and user-friendly, meeting modern digital communication expectations.
Analytics Driven UI Improvements
Data-driven insights can inform continuous improvement of frontend for chatbots. Metrics such as drop-off points, response time, click patterns, and engagement rates highlight interface areas needing adjustment. Designers can optimize layout, input options, and message presentation based on observed behavior. Interactive dashboards integrated within the frontend allow real-time monitoring of user interactions, helping teams respond quickly to issues. Analytics not only enhance efficiency but also reveal trends in user preferences, guiding strategic design decisions. By incorporating analytics into the frontend design cycle, chatbots evolve with their audience, becoming more intuitive, responsive, and aligned with user expectations.
Conversational Analytics and Frontend Optimization
A well-designed frontend for chatbots not only guides user interactions but also enables valuable data collection. By monitoring engagement patterns, drop-off points, and frequently selected responses, businesses can refine conversation flows and UI elements for better performance. Integrating analytics into the frontend for chatbots allows teams to understand how users navigate the interface, which prompts are most effective, and where improvements are needed. This data-driven approach ensures the chatbot evolves with user behavior, enhancing both usability and satisfaction. A frontend optimized with analytics helps maintain a seamless experience, encourages deeper engagement, and ultimately boosts the effectiveness of AI-driven chatbots in real-world applications.
Scalability and Modular Frontend Design

As chatbots grow in functionality, the frontend must scale accordingly. Modular design principles in the frontend for chatbots allow developers to add new features, message types, or interactive elements without disrupting existing workflows. Components like reusable buttons, adaptive layouts, and flexible input fields ensure consistent performance across updates. Scalability also involves preparing for higher user loads while maintaining responsive interactions. A well-structured, modular frontend for chatbots supports continuous improvement, experimentation, and integration with emerging technologies. By anticipating growth, businesses ensure the conversational interface remains intuitive, engaging, and capable of delivering high-quality user experiences, even as complexity increases over time.
Conclusion
A well-designed frontend for chatbots is the cornerstone of successful conversational experiences. It transforms complex AI interactions into intuitive, user-friendly conversations, enhancing engagement, trust, and satisfaction. By integrating responsive UI, adaptive layouts, real-time feedback, and accessibility, businesses ensure users navigate dialogues effortlessly. Modern chatbots that combine personalized interfaces, multi-modal interactions, and analytics-driven improvements create more meaningful and productive exchanges. Investing in the frontend for chatbots not only boosts user retention but also amplifies the effectiveness of AI-driven marketing, support, and informational services, ultimately driving better outcomes for both users and organizations.
Frequency Asked Question (FAQ)
What is the frontend for chatbots?
The frontend for chatbots is the user-facing interface that allows people to interact with a chatbot. A good frontend for chatbots includes message layouts, input fields, buttons, and visual cues that guide conversations smoothly.
Why is frontend design important for chatbots?
A strong frontend for chatbots enhances usability, engagement, and trust. It ensures conversations are smooth, intuitive, and responsive, turning AI interactions into meaningful experiences for users.
How does chatbot UI design affect user engagement?
Chatbot UI design, a core part of the frontend for chatbots, organizes messages, buttons, and visual feedback to reduce friction, guide interactions, and keep users actively participating, boosting satisfaction and completion rates.
Can frontend design impact marketing results?
Yes. A well-crafted frontend for chatbots supports AI-driven chatbot marketing by providing intuitive navigation, personalized experiences, and clear calls-to-action, increasing conversions and engagement effectively.
How do I make a chatbot frontend more accessible?
Use screen reader support, keyboard navigation, clear contrast, readable fonts, and responsive layouts. An accessible frontend for chatbots ensures inclusive interactions for all users without compromising usability.
Should chatbots support voice interaction in the frontend?
Absolutely. Voice-activated chatbots combined with visual cues in the frontend for chatbots create multi-modal experiences, improving convenience, accessibility, and engagement across different user preferences.






AI Chatbots for Customer Retention Management
Transforming Employee Onboarding with AI Chatbots: A Step-by-Step Guide
Emergency Response Chatbots: Revolutionizing Crisis Management with AI
Revolutionizing Recruitment: How Chatbots Streamline Hiring Processes and Elevate Talent Acquisition